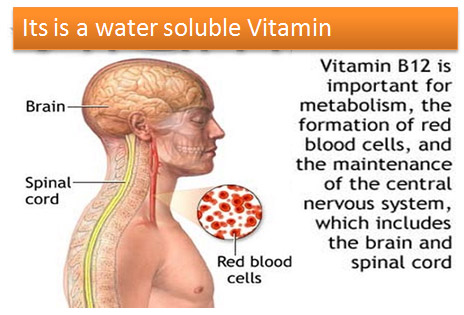
What is Vitamin B12
Methylcobalamin is also called as Vitamin B12. It is a water-soluble vitamin that is naturally present in some foods, added to others, and available as a dietary supplement and a prescription medication. Vitamin B12 exists in several forms and contains the mineral cobalt, so compounds with vitamin B12 activity are collectively called “cobalamins”. Methylcobalamin and 5 - deoxyadenosylcobalamin are the forms of vitamin B12 that are active in human metabolism. Vitamin B12 is required for proper red blood cell formation, neurological function, and DNA synthesis.
Natural Sources of Vitamin B12

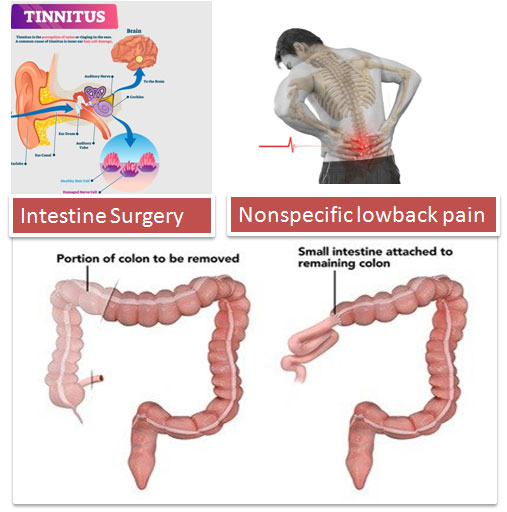
Deficiency of Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 deficiency is characterized by megaloblastic anaemia, fatigue, weakness, constipation, loss of appetite, and weight loss. Neurological changes, such as numbness and tingling in the hands and feet, can also occur. Additional symptoms of vitamin B12 deficiency include difficulty in maintaining balance, depression, confusion, dementia, poor memory, and soreness of the mouth or tongue. The neurological symptoms of vitamin B12 deficiency can occur without anaemia, so early diagnosis and intervention is important to avoid irreversible damage.
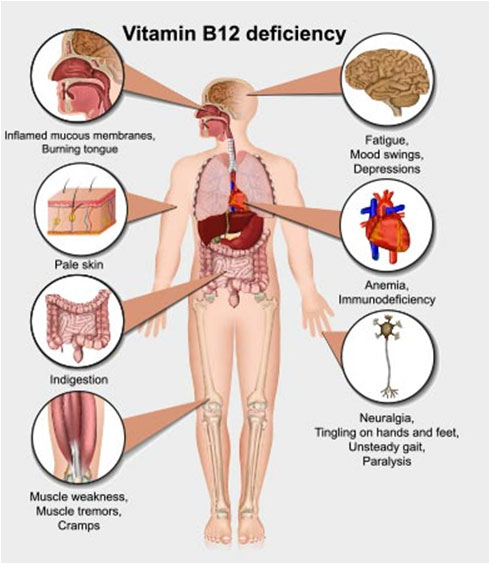
Reasons for Vitamin B12 deficiency
- Lack of intrinsic factor.
- Pernicious anaemia.
- Surgery in the gastrointestinal tract.
- Prolonged use of certain medications (e.g., metformin or proton pump inhibitors)
- Hereditary intrinsic factor defects and congenital problems.
- Vegan diet.
- Malaborption syndrome.
- Alcoholism.Liver diseases.
- Smoking.
- Use of oral contraceptives.
What is Subneuro Sublingual
Subneuro (Methylcobalamin) Sublingual Route a New Advance Sublingual, literally 'under the tongue', from Latin, refers to a pharmacological route of administration in which certain drugs are entered directly into the bloodstream via absorption under the tongue.
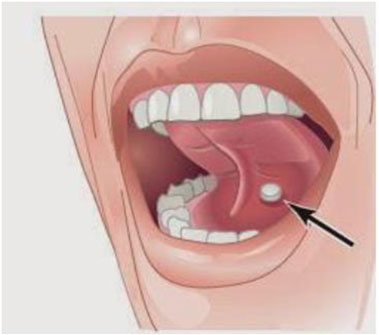
Put the Subneuro Tablet below the Tongue
What is Principle of Subneuro Sublingual
The principle behind sublingual administration is fairly simple. When a chemical comes in contact with the mucous membrane, or buccal mucosa, it diffuses into the epithelium beneath the tongue. This region contains high density of blood vessels, and as a result, via osmosis, the substance quickly enters the blood stream to produce therapeutic effect. Since the venous drainage from the mouth is to the superior vena cava, the drug also is protected from rapid hepatic first pass metabolism, which is sufficient to prevent the appearance of any active drug in the systemic circulation if the sublingual tablet is swallowed. (For absorption of Vitamin B12, intrinsic factor is needed. For patients having deficient intrinsic factor or gastric problem intramuscular injections are preferred, now a day’s Sublingual is best option available as Intramuscular injections are very painful)
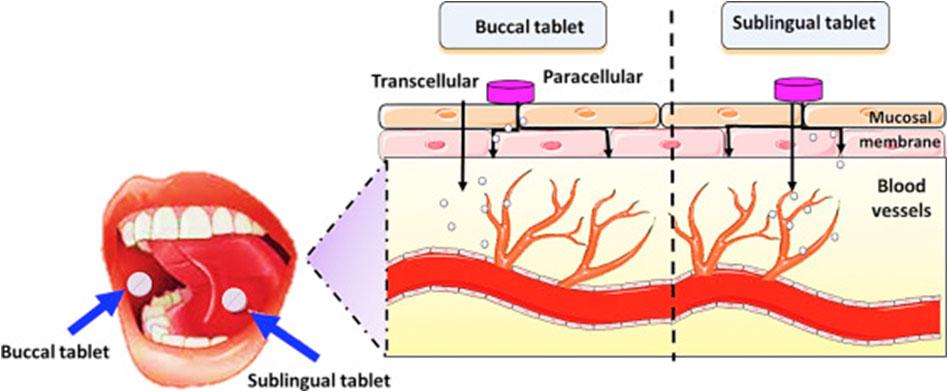
Therapeutic advantages of Sublingual Subneuro
Sublingual routes of administration have certain advantages over simple oral administration. This route is often faster and it also shows quick onset of action, minimized side effects of the drugs because the drug bypasses the gastrointestinal tract and better therapeutic level of drug can be achieved by this route. In nut shell fast absorption, immediate action with maximum bioavailability.

Other advantages of Subneuro Sublingual